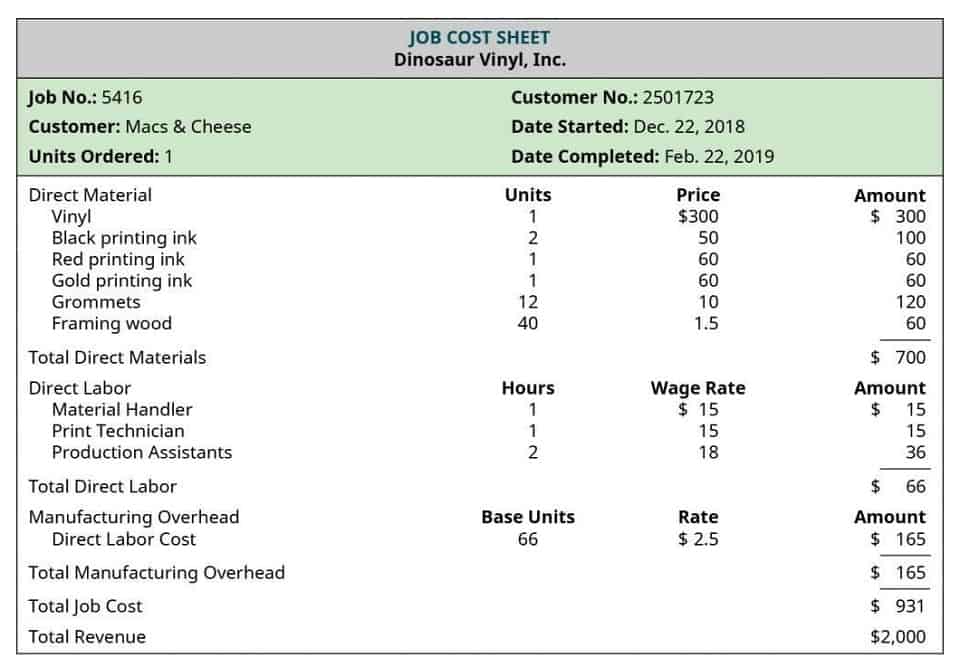
A savvy investor knows how to use accounting ratios to determine whether a stock presents a lucrative opportunity or perhaps a liability that other investors have yet to realize. The financial reports that accounting ratios are based on represent much of the core essence of a business. They paint a picture of where a company came from, how they are doing currently, and where they are going into the future. The ratios may seem simple at first, but they are incredibly nuanced and can be difficult to calculate once one is attempting to analyze and quantify Fortune 500 companies.
Want More Helpful Articles About Running a Business?
This is the “assets” portion of the balance sheet, or the entire top portion of it. Accounts payable and accounts receivable are both accrual types. To further illustrate the analysis of transactions and their effects on the basic accounting equation, we will analyze the activities of Metro Courier, Inc., a fictitious corporation. Refer to the chart of accounts illustrated in the previous section. Shareholder Equity is equal to a business’s total assets minus its total liabilities. It can be found on a balance sheet and is one of the most important metrics for analysts to assess the financial health of a company.
Accounting Equation Formula
By contrast, the alternate method of cash basis accounting would only record that $1,000 as revenue when the customer actually paid for the purchase. In general, large businesses and publicly traded companies favor accrual accounting. Small businesses and individuals tend to use cash basis accounting. Each accounting period covers one complete accounting cycle.
- They paint a picture of where a company came from, how they are doing currently, and where they are going into the future.
- Likewise, revenues increase equity while expenses decrease equity.
- To learn more about the income statement, see Income Statement Outline.
- In the coming sections, you will learn more about the different kinds of financial statements accountants generate for businesses.
What are Accounting Ratios?
After six months, Speakers, Inc. is growing rapidly and needs to find a new place of business. Ted decides it makes the most financial sense for Speakers, Inc. to buy a building. Since Speakers, Inc. doesn’t have $500,000 in cash to pay for a building, it must take out a loan. Speakers, Inc. purchases a $500,000 building by paying $100,000 in cash and taking out a $400,000 mortgage. This business transaction decreases assets by the $100,000 of cash disbursed, increases assets by the new $500,000 building, and increases liabilities by the new $400,000 mortgage.
Single-entry systems also account only for revenues and expenses. Double-entry systems add assets, liabilities, and equity to the financial tracking. Working capital defines the sum that remains after subtracting current liabilities from current assets. https://www.bookstime.com/articles/net-sales Equity capital specifies the money paid into a business by investors in exchange for stock in the company. Debt capital covers money obtained through credit instruments such as loans. The third part of the accounting equation is shareholder equity.
Assets Always Equal Liabilities Plus Equity

The income statement is the financial statement that reports a company’s revenues and expenses and the resulting net income. While the balance sheet is concerned with one point in time, the income statement covers a time interval or period of time. The income statement will explain part of the change in the owner’s or stockholders’ equity during the time interval between two balance sheets. If a company keeps accurate records using the double-entry system, the accounting equation will always be “in balance,” meaning the left side of the equation will be equal to the right side. The balance is maintained because every business transaction affects at least two of a company’s accounts.

- Fortunately, in the real world, you’ll only need to use a fraction of the accounting math you learned in school.
- This equation holds true for all business activities and transactions.
- Single-entry systems also account only for revenues and expenses.
- In accounting, we have different classifications of assets and liabilities because we need to determine how we report them on the balance sheet.
- The accounting equation is fundamental to the double-entry bookkeeping practice.
- If the left side of the accounting equation (total assets) increases or decreases, the right side (liabilities and equity) also changes in the same direction to balance the equation.
These may include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bond issues, warranties, and accrued expenses. The accounting equation helps to assess whether the business transactions carried out by the company are being accurately reflected in its books and accounts. This straightforward relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity is considered to be the foundation of the double-entry accounting system. The accounting equation ensures that the balance sheet remains balanced.
- Here are our top six formulas to help you stay on top of your small-business accounting.
- This number is the sum of total earnings that were not paid to shareholders as dividends.
- Said a different way, liabilities are creditors’ claims on company assets because this is the amount of assets creditors would own if the company liquidated.
- These are fixed assets that are usually held for many years.
The Basic Accounting Equation
There are different categories of business assets including long-term assets, capital assets, investments and tangible assets. They were acquired by borrowing money from lenders, receiving cash from owners and shareholders or offering goods or services. Let’s move ahead so that you can gain a more detailed understanding of the basic accounting equation and its components. The basic accounting formula accounting basic formula is one of the fundamental underpinnings of accounting, since it forms the basis for the recordation of all accounting transactions. In essence, if both sides of the basic accounting formula do not match at all times, there is an error in the accounting system that must be corrected. The concept of expanded accounting equation is that it shows further detail on where the owner’s equity comes from.

Overhead costs must be recouped through revenues for a business to become or remain profitable. Major examples of the individual accounts found in a general ledger include asset accounts, liability accounts, and equity accounts. Each transaction recorded in a general ledger or one of its sub-accounts is known as a journal entry. Accountants use “initial inventory plus purchases, minus ending inventory” as a basic accounting formula for calculating COGS over a specific accounting period. Small business owners and individual taxpayers can also benefit from a strong working knowledge of basic accounting concepts and terms. Accounting advances financial literacy and yields precise, powerful insights into financial health.

